2.2 STRUKTUR ATOM Model Atom Thomson nyatakan bahawa atom berbentuk sfera sfera ini ada cas positif atau proton dan cas negatif yang disebut elektron elektron da proton terdapat secara bertaburan dalam sfera atom unsur yang berlainan ada bil elektron dan bil proton yang berlainan beliau kata jisim elektron ialah 2000 kali ganda lebih ringan. Each of these elements has a distinct and characteristic chemistry. In the neutral atom, the value of Z ALSO gives the number of the electrons that are conceived to orbit the nuclear core. In the nucleus itself, there may be as many protons or less AS neutrons, massive particles of zero electronic charge. A proton is a positively charged subatomic particle within the atomic nucleus of atoms. The number of protons in the atomic nucleus is what determines the atomic number of an element, as indicated in the periodic table of the elements. The proton is not an elementary particle but a compound particle. All matter, including mineral crystals, is made up of atoms, and all atoms are made up of three main particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. As summarized in Table 2.1, protons are positively charged, neutrons are uncharged and electrons are negatively charged. The negative charge of one electron balances the positive charge of one proton.
Atom
The smallest partical of the element, which remain the properties of the element.
OR
Atom is a Greek word and its means is particle, so atom is smallest particle of the mater, which has properties of element. E.g. Iron, Al, cu, etc
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the characteristics of that element. According to the classical Bohr model, atoms have a planetary type of structure that consists of a central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. The nucleus consists of positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. A Short description about these particles is given below.
FUNDAMENTAL PARTICLES OF THE ATOM
- ELECTRON
- PROTON
- NEUTRON
ELECTRON

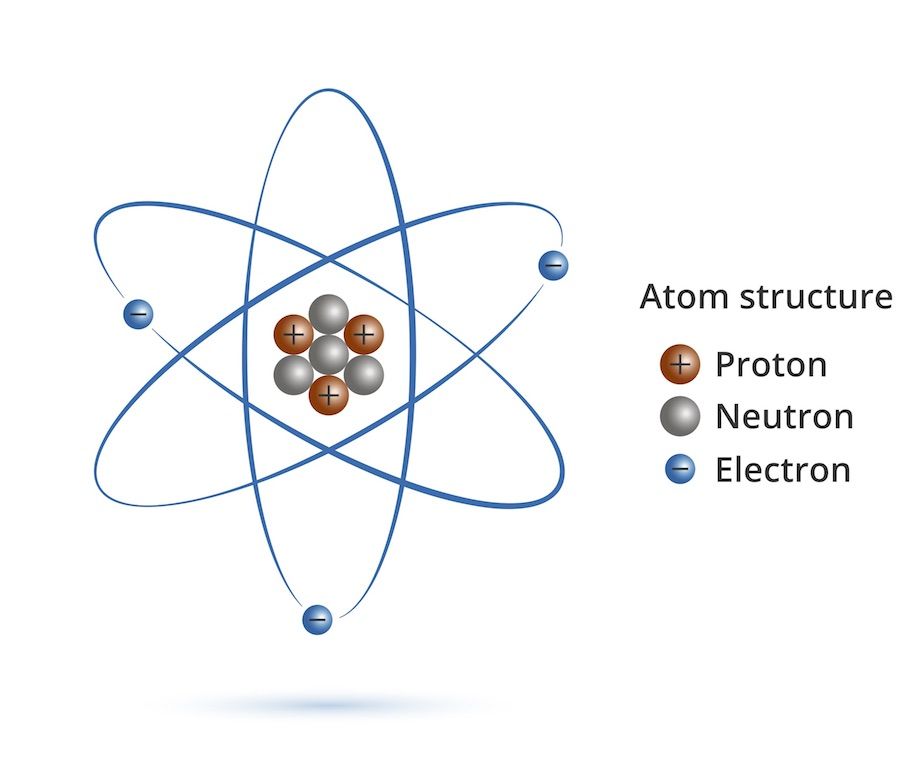
It also a fundamental particle of the atom. Electron is a particle which has negative charge. It is negative charge. The amount of the charge is -1.6x10-19 coulomb. Mass of electron is 9.11x10-31 kg or 0.00054859 a.m.u. Since atom has equal number of electrons and protons and they have equal and opposite charges hence they cancel their effect and atom becomes neutral. It is 1836 times lighter than proton. It is revolving around the nucleus.
PROTON

Proton Atom Location
Proton is a particle which has positive charge.It is inside the nucleus. The amount of charge is 1.6x10-19 coulomb. The mass of proton is 1.67x10-27 kg or 1.0072766 a.m.u. It is 1836 times heavier than electron. The number of protons and electrons are equal in an atom.
NEUTRON
Neutron is a neutral particle thus it has not any charge. Hence the name Neutron is derived form the word neutral. It is heavier than electron. It mass is nearly equal to the mass of proton that is equal to 1.6x10-27kg or 1.0086654 a.m.u. It is 1842 times heavier than electron.both the proton and neutron make the atomic mass of the atom. It resits in site the nucleus.
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
We know that electron is revolving around the nucleus in different position. These positions are called energy levels or shell electrons are distributed among the shell according to 2(N)2 formula.
The number of electron in K shell 2N2 = 2(1)2 = 2
The number of electron in L shell 2N2 = 2(2)2 = 8
Proton Atom Location
The number of electron in M shell 2N2 = 2(3)2 = 18 Etc, etc
The number of electron in the outer most shell is not distributed 2(N) 2 formula. The outer most shell is called valance shell and the electron in it are called valence electron.
Proton Atomic Location
FOR EXAMPLE (CU)
ATOMIC NUMBER = 29
Proton Atomic Number
The number of electron in K Shell = 2(1) = 2
The number of electron in L shell = 2(2)2 = 8
The number of electron in M shell = 2(3)2 = 18
The number of electron in N shell = 1
